THYROID DISORDERS
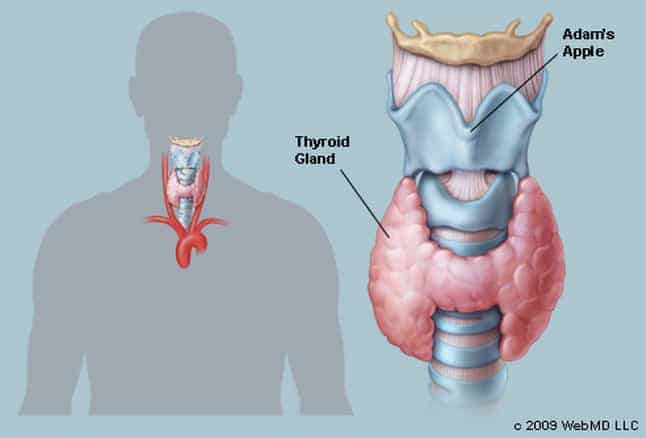
Thyroid gland is a butterfly shaped gland in the front of the neck .
The thyroid has important roles to regulate numerous metabolic process throughout the body .
Different types of disorders affects either its structure or function.
The Thyroid gland is located below the Adam’s apple wrapped around the trachea (windpipe).
A thin area of tissue in the gland ‘s middle.known as the isthmus ,joins the two thyroid lobes on each side.
The Thyroid uses iodine to produce vital hormones.Thyroxine , also known as T4, is the primary hormone produced by the gland .
After the delivery via the bloodstream to the body’s tissues, a small portion of the T4 released from the gland is converted to triiodothyronine(T3),which is the most active hormone
The Thyroid gland is regulated by a feedback mechanism involving the brain.
When Thyroid hormone levels are low , the hypothalamus in the brain produces hormone known as thyrotropin releasing hormone(TRH) that causes the pituitary gland (located at the base of the brain ) to release thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH).
TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to release more T4.
Since the thyroid gland is controlled by the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, disorders of these tissues can also affect thyroid function and cause thyroid problems.
Several different disorders can arise when thyroid produces too much hormones (hyperthyroidism) or not enough (hypothyroidism).
Four common disorders of the thyroid are:-
- Hashimoto’s disease
- Graves disease
- Goiter
- Thyroid nodules
- Thyroid cancer
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism results from the thyroid gland producing an insufficient amount of thyroid hormone.
it can develop from problems within the thyroid gland, pituitary gland ,or hypothalamus.
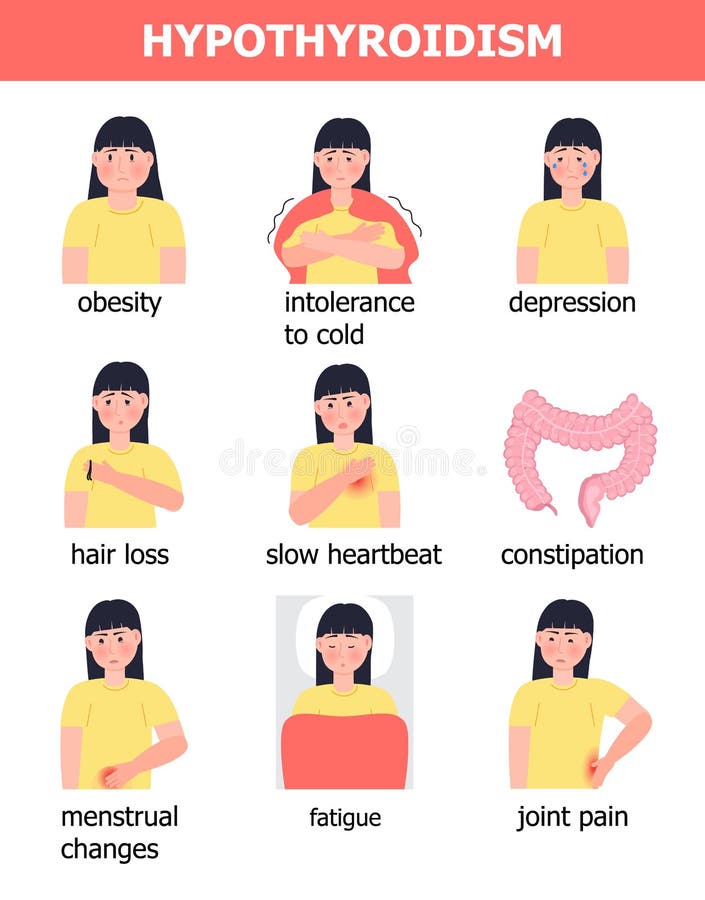
Symptoms of hypothyroidism can include:-
- Fatigue
- Poor concentration or feeling mentally” foggy”.
- Dry skin
- Constipation
- Feeling cold
- Fluid retention
- Muscle and joint aches
- Depression
- prolonged or excessive menstrual bleeding in women
Some common causes of hypothyroidism include
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (an autoimmune condition that causes inflammation of the thyroid gland)
- Thyroid hormone resistance
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a result of excessive production of thyroid hormone, a less common condition than hypothyroidism.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism usually relate to increased metabolism .
In mild cases ,there may not be apparent symptoms.
Symptoms and signs of hyperthyroidism can include:-
- Tremor
- Nervousness
- Tachycardia
- Fatigue
- Intolerance for heat

- increase bowel movements
- Excessive sweating
- Lack of concentration
- Sudden loss of weight
The most common causes of hyperthyroidism are:-
- Graves’ disease
- Toxic multi nodular goiter
- Thyroid nodules that over express thyroid hormone (known as hot nodules)
- Excessive iodine consumption
Goiter
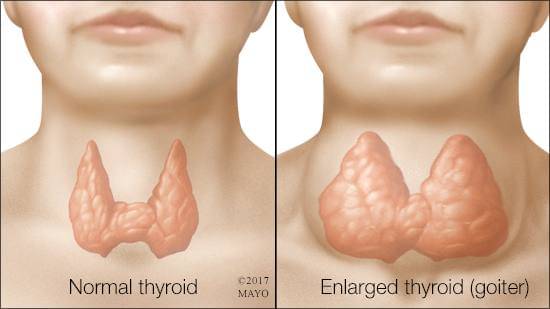
A goiter simply describes enlargement of the thyroid gland, regardless of cause. A goiter is not a specific disease .
A goiter may be associated with hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, or normal thyroid function.
Thyroid Nodules:-
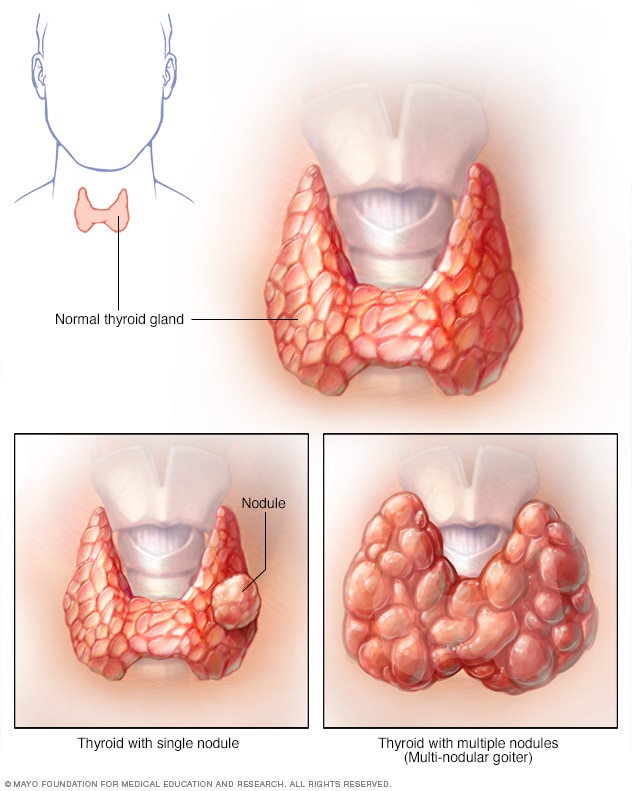
Nodules are lumps or abnormal masses within the thyroid.
Nodules can be caused by benign tumors or less commonly by cancers of the thyroid.
Nodules may be single or multiple and can vary in size.
If nodules are excessively large, they ma cause symptoms related to compression of nearby structures.
Thyroid Cancer:-
Thyroid cancer is far more common among adult women than men or youth.
About 2/3 of cases occur in people under age 55.
There are different kind of thyroid cancer ,depending upon the specific cell type with in the thyroid that has become cancerous
Most cases of thyroid cancer have good prognosis and high survival rate especially when diagnosed in its early stages
Diagnosis:-
- Medical history
- Physical examination of patient
- Blood test :- Thyroid profile
- Antibodies test :-titers of anti-thyroglobulin, anti – thyroperoxidase , or TSH receptors stimulating antibodies
- Imaging tests to rule out thyroid nodules or enlargement
- USG (ultra sonography ) of neck :- visualise the consistency of the tissue within the gland and can often reveals cysts or calcification
- Thyroid scans using radioactive iodine are often performed to evaluate the function of thyroid nodules.
- The thyroid is the only gland in the body that take up iodine ,so when radioactively labeled iodine is given it is taken up by the thyroid gland .
- An imaging test typically shows uptake of radioactive iodine by normal thyroid tissue .areas of nodules that are producing excess hormone [referred to as hyper functioning ]will show an increased uptake of iodine.These are referred to as “hot”nodules or areas.
- By contrast so called “cold”nodules represents areas with decreased iodine uptake .
- Cold nodules do not produce excess hormone and can sometimes represents cancer.
- Fine needle aspiration and biopsy are technique that remove a sample of cells or tissues frome thyroid gland for examination and diagnosis by a pathologist, who is a physician trained in the diagnosis of condition based on tissues sample
- Fine needle aspiration uses a long thin needle to withdraw a sample of cells from the thyroid
- FNA can be performed in the doctor’s office sometimes , ultrasound imaging to use the FNA procedure .
- A biopsy is the surgical sampling of a tissue.
Treatment:-
Thyroid disorders can be treated by medications, or in some cases ,surgery
Treatment will depend on the particular disease of the thyroid.
Thyroid Medication:-
Medication can be given to replace the missing thyroid hormone in hypothyroidism.
Synthetic thyroid hormone is given in pill form orally.
For hyperthyroidism medication can be used to decrease production of thyroid hormone or to prevent its release from the gland .
if hyperthyroidism is not control with medication ,radioactive ablation ican be performed.
Ablation involve giving doses of iodine labeled with radioactivity that selectively destroys the thyroid tissue.
Thyroid Surgery:-
Surgery can be used to remove a large goiter or a hyper functioning nodules with in the gland .
Surgery is necessary when there is a possibility of thyroid cancer.
If the thyroid gland is removed entirely , the individual will need to take synthetic thyroid hormone for life .
Thyroid surgery can be also be used in Graves Disease(subtotal thyroidectomy) and was the treatment of choice prior to RAI therapy and anti – thyroid medications.
Prognosis:-
In most cases , thyroid disorders can be well managed with medical treatment and are not life threatening .
Some conditions may require surgery .
Prognosis for most cases of thyroid cancer is also good.
Patient with thyroid cancer that has spread throughout the body have a poorer prognosis.